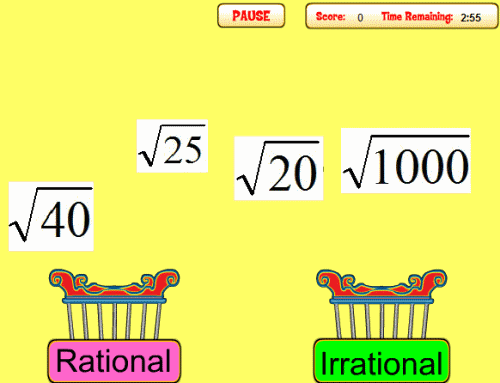
Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number.
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., sqrt(2)). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of sqrt(2), show that sqrt(2) is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations.
| Screenshot | Name / Description | Flag? | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Rational BIns Identify rational and irrational numbers. |
 |
|