Understand that the probability of a chance event is a number between 0 and 1 that expresses the likelihood of the event occurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood. A probability near 0 indicates an unlikely event, a probability around 1/2 indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and a probability near 1 indicates a likely event.
Approximate the probability of a chance event by collecting data on the chance process that produces it and observing its long-run relative frequency, and predict the approximate relative frequency given the probability. For example, when rolling a number cube 600 times, predict that a 3 or 6 would be rolled roughly 200 times, but probably not exactly 200 times.
Develop a probability model and use it to find probabilities of events. Compare probabilities from a model to observed frequencies; if the agreement is not good, explain possible sources of the discrepancy.
Find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulation.
| Screenshot | Name / Description | Flag? | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
|
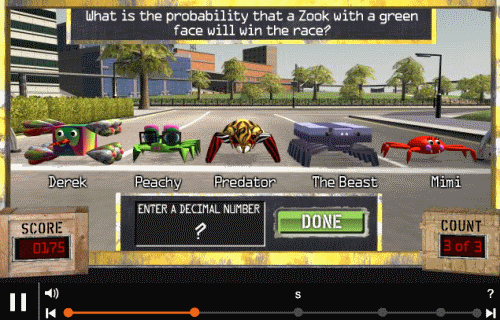
Bamzooki Zooks Practice probabilities with the Zooks! |
 |
|
|
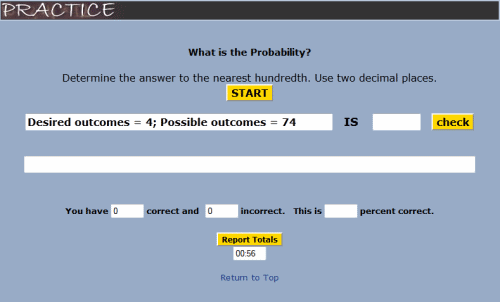
Probability Practice Practice simple probability statements given desired and possible outcomes. |
 |
|
|
Probabilities Quiz Show Multiple teams can play this quiz show game with probabilities. |
 |
|