Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 x 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 x 7.
Interpret whole-number quotients of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 56 / 8 as the number of objects in each share when 56 objects are partitioned equally into 8 shares, or as a number of shares when 56 objects are partitioned into equal shares of 8 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a number of shares or a number of groups can be expressed as 56 / 8.
Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.
Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 x ? = 48, 5 = _ / 3, 6 x 6 = ?
| Screenshot | Name / Description | Flag? | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|

|
Khan - Associative Law of Multiplication Work through a practice problem on the associate law (2:15) |
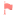 |
|
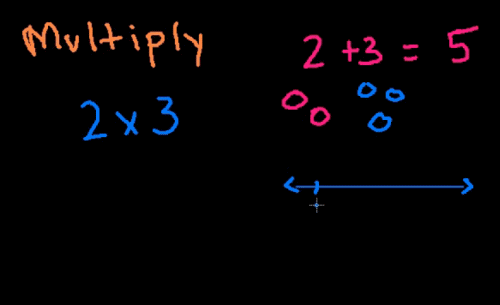
|
Khan - Multiplication 1 Introduction to multiplication via grouping objects (13:20) |
 |
|
|
Khan - Division 1 Introduction to division with Sal (17:02) |
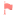 |
|
|
Khan - Division 2 Second part of an introduction to division (11:39) |
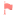 |
|
|
Khan - Division 3 Part three in this three part series on division - includes remainders (10:07) |
 |
|